Sustainability Nexus AID: storms
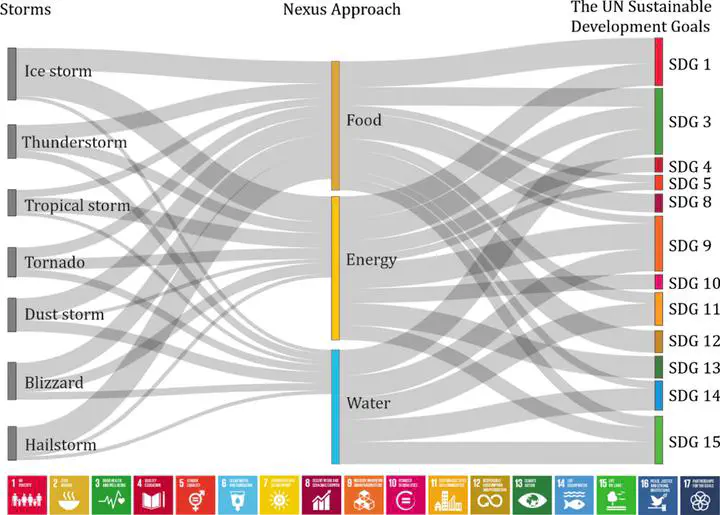 The Sankey diagram illustrating the need for a Nexus approach in mitigating storm-related threats and advancing progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Sankey diagram illustrating the need for a Nexus approach in mitigating storm-related threats and advancing progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)Abstract
Storms include a range of weather events resulting in heavy liquid and solid precipitation and high winds. These events critically impact crops and natural resources and, in turn, health, economy, and infrastructure safety. The intensity and frequency of the physical mechanisms triggering storms will most likely increase under global warming due to the changing flows of water and energy in the atmosphere. Addressing storm threats holistically requires a nexus approach that links climate change, infrastructure, and human prosperity and well-being, contributing to achieving the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. This work introduces the Storms Module of the United Nations University (UNU) Sustainability Nexus Analytics, Informatics, and Data (AID) Programme. The paper aims to emphasize the importance of AID tools in addressing storm impacts through a data-driven nexus approach that recognizes the connections between storm hazards, policy, and society. Today, AID tools are instrumental in understanding storms and making informed decisions to manage them. AID tools contribute to archiving and monitoring storm data, employing predictive models and early warning systems, estimating storm risk, conducting post-storm analysis, and aiding preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. The Storms Module lists freely available AID tools, including large databases, simulation and precipitation tools, and resources for storm preparedness. Over the next years, new Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies, are expected to revolutionize storm understanding, forecasting, and adaptive planning. However, especially for the operational use of new AI tools, caution is advised due to potential limitations regarding data quality, ethical concerns, cybersecurity risks, and the need for legal frameworks.