Abstract
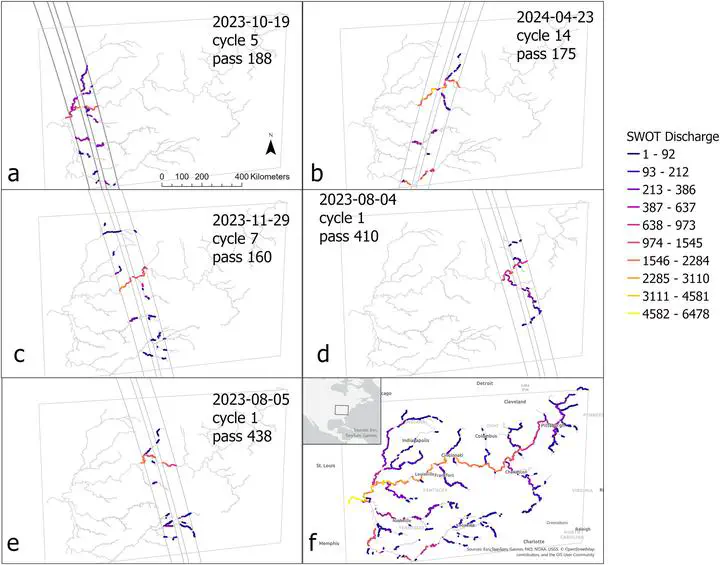
The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite has the potential to transform global hydrologic science by offering simultaneous and synoptic estimates of river discharge and other hydraulic variables. Discharge is estimated from SWOT observations of water surface elevation, width, and slope. A first assessment using just the highest quality SWOT measurements, over the first 15 months (March 2023–July 2024) of the mission evaluated at 65 gauged reaches shows results consistent with pre-launch expectations. SWOT estimates track discharge dynamics without relying on any gauge information: median correlation is 0.73, with a correlation interquartile range of 0.51–0.89. SWOT estimates capture discharge magnitude correctly in some cases but are biased (median bias is 50%) in others. There are already a total of 11,274 ungauged global locations with highest quality SWOT measurements where SWOT discharge is expected to accurately track discharge variations: this value will increase as SWOT data record length grows, algorithms are refined and SWOT measurements are reprocessed. This first look indicates that SWOT discharge is performing as expected for SWOT data that achieve performance requirements, providing observed information on discharge variations in ungauged basins globally.